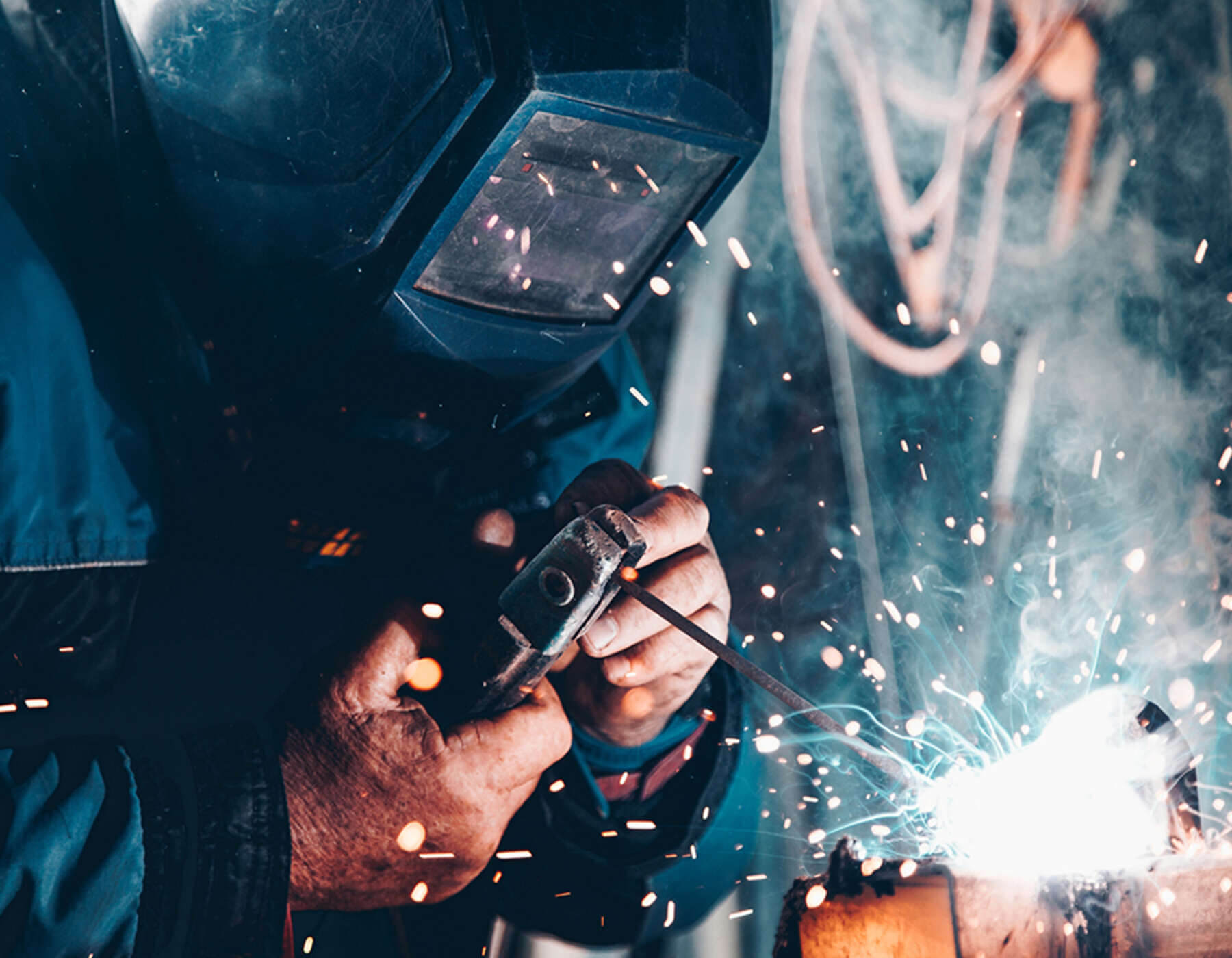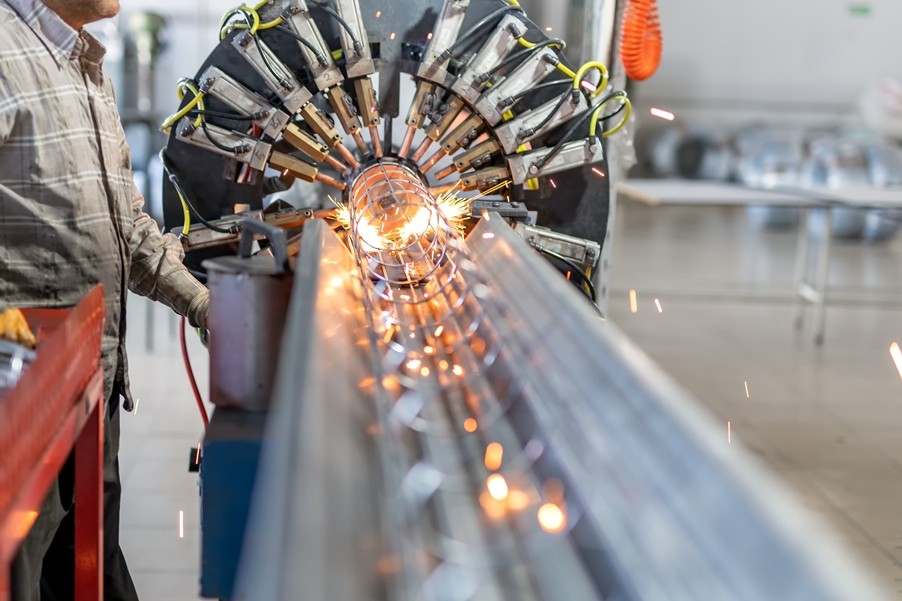
Another popular form of welding that the Morfabrication team often uses on specific projects is stud welding.
A process that secures a stud (fastener) to a base metal by using a stud welding gun to heat both parts and secure the fastener in place.
Stud welding comes with many benefits, and it’s important to understand the differences between stud welding and some of its counterparts to distinguish which welding process is the most suitable for meeting your project requirements.
Stud Welding Definition
Fasteners (stud welds) are used and placed onto the base metal to create a permanent, high-strength bond.
Stud welding is a process that allows sheet metal fabricators to attach studs to sheet metal in one swift movement and shot from a stud welding gun—securing the bond in place and creating a strong and reliable connection.
For sheet metal fabricators, what is interesting to note is that with this type of welding, the base metal and the welded stud can be made of different materials. For example brass to copper, copper to steel, etc. This makes it an extremely flexible and versatile weld type.
The most popular type of stud welding is stud arc welding which we will explore in more detail below..
Stud welding is suitable for buildings and bridges, cable management, applications within the
food sector, automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, construction, and more, as it maintains structural integrity supporting products such as:
- Pipes
- Switches
- Hatches
- Buttons
- Brackets
- Handles
- Signs
- Badges
- Homeware, and even
- Jewellery
Procedures of Stud Welding
To get started with stud welding, you will need the following:
- A stud welding tool/gun.
- Metal fasteners – fasteners can be threaded, unthreaded, and tapped and can be of any material, for example, steel, stainless steel, aluminium, copper, and more.
- Stable power supply.
- Sheet metal fabrication near me – working with professional and experienced fabricators is your best option for achieving a successful and high-quality product outcome.
From here:
Start by cleaning and removing any dirt and debris from around the weld point; you don’t want anything to contaminate the weld or affect its quality.
Secondly, make sure to use the right tools and equipment and ensure all of these are available at the right time.
Third, choose the right process for your product and project. See below for further details on the stud welding process.
Finally, make sure you have all of the correct and appropriate safety equipment in place.
Process of Stud Welding
Stud arc welding – arc welding involves heating both the base material and the stud to create a bond using an arc of electricity.
Note: Stud arc welding involves no filler material; it simply requires pressure from the stud welding gun to fuse the metal fastener to the base material.
By attaching the weld studs to the sheet metal and using the arc, when both the fastener and the base metal become molten, pressure can be applied to the fastener to sink it into the workpiece using the welding gun.
From here, the weld will be left to cool and set, with any remnants of the weld removed for a neat finish.
Stud arc welding suits materials over 2mm thick and those with larger diameter studs.
It provides a neat and controlled weld that is much more flexible than its spot weld counterpart.
Stud arc welding is most suited to steel alloys and aluminium.
Capacitor discharge stud welding – another process of stud welding. When the stud is placed onto a metal sheet (typically a thin gauge), the charged capacitor will then discharge high current pulses to heat and melt the stud and, similar to above, produce an arc. The stud will then melt into the sheet metal, providing the bond. This particular process of stud welding is most suitable for smaller-diameter studs and materials that are 0.7mm thick.
Capacitor discharge stud welding is most suited to copper-based metals due to the levels of heat conductivity.
Stud welding is the perfect solution for creating beams, door jams, decorative consumer items, electrical goods, furniture, heating and ventilation applications, and more.
Benefits of Stud Welding
Stud welding is:
- Reliable
- Suitable for a wide range of applications
- A quick welding process (easy to install), making it less expensive.
- Able to provide maximum weld penetration
- Strong and secure (unlike some welds, a stud weld won’t be able to work itself free)
- A one-sided weld, making it suitable for use in a variety of locations as you only need access to one side, meaning no punching or deburring holes, so there are no issues with leaks or stains.
- Aesthetically pleasing
- Suitable for sheet metals of varying types and thickness
- A welding procedure that can be automated, saving you considerable time and resources. Automated stud welds use CNC machinery to maximise accuracy and efficiency. Automating such processes also helps to reduce human error and improve overall safety.
Sheet Metal Fabricators UK
Stud welding is one of many types of welding procedures that our team has experience in using. Providing you with fast, reliable, and high-quality results, we support your project across all aspects of fabrication.
Manufacturing a range of fabricated goods and services, we use our years of experience, knowledge, and dedication to provide the highest-quality solutions to ensure you receive a first-class service from us every time.
This, along with our competitive prices, is why so many customers return to us as their fabricator of choice.
Got a question?
Contact us for your next stud welding project.
